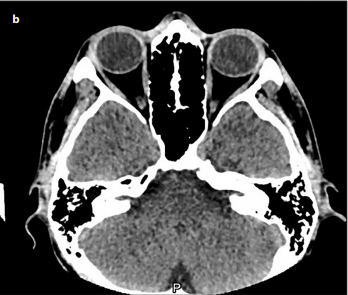
There are some orbital and intracranial complications of acute and chronic inflammation of paranasal sinuses. Some fatal complications can be encountered despite the wide use of antibiotics. Periorbital cellulitis occurs as a result of inflammation of ethmoid sinuses and is mostly seen in childhood. This clinical condition is characterized by swelling, redness, and ocular pain but the vision is unaffected. A 16-year-old boy with amblyopia on the left eyeball was admitted to our outpatient clinic with a complaint of a headache lasting for two days. Medical treatment was started with the diagnosis of acute sinusitis. In the second day of treatment, the patient was admitted to our clinic because of swelling, redness, and pain on the right eyeball and was hospitalized with the diagnosis of right periorbital cellulitis. Despite using two different intravenous antibiotics, the patient’s visual acuity was decreased and his eyeball movements’ limitation was increased within hours. The patient did not respond to treatment and therefore subperiosteal orbital abscess was drained surgically. It is important to consider the age and other conditions of a patient to decrease mortality and morbidity when treating a patient with swelling of the eyelids. Sinusitis is a common disease that may cause an orbital abscess, epidural abscess, and intracranial complications.
Cite this article as: Aksoy A, Özata Güngör Ö, Zor KR. Orbital Abscess in the Case of Amblyopia. Eur J Rhinol Allergy 2019; 2(3): 92-4.

.png)

.png)