Abstract
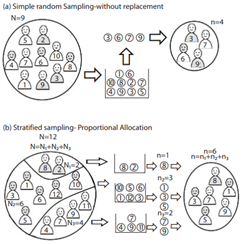
Objective: Researchers are rarely able to sample the entire population of interest in health science studies, owing to a large number of subjects. In such situations, the researcher studies a sample obtained from the target population and applies the findings from the sample to infer conclusions about the related population. Obtaining valid and reliable results is completely dependent on the selection of an appropriate sampling method. The aim of this study is to inform readers about the most common sampling methods and to investigate the level of knowledge of physicians working with academic staff.
Material and Methods: A total of 104 medical academic staff members participated in our study. We obtained data using a questionnaire and by conducting a face-to-face interview.
Results: While 26.92% of the participants correctly answered the question on the simple random sampling, only 8.65% and 2.88% of the participants correctly answered the questions on stratified sampling and systematic sampling, respectively. No significant difference was noted in terms of matching correct sampling methods by academic category.
Conclusion: In health science, obtaining reliable results can be achieved by using statistical methods during the planning stage as part of the concluding stages of the study. Biostatistics experts should be consulted at every stage of the study.
Cite this article as: Can FE, Ercan İ, Sığırlı D, Kaya MO, Uysal Ö. Basic Sampling Methods: What is the Knowledge Level of Academic Staff? Eur J Rhinol Allergy 2019; 2(1): 1-5.

.png)

.png)