Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to elucidate the effect of Staphylococcus aureus and budesonide on the mRNA expression and the biologic role (caspase-1 activation and IL-1β secretion) of NLRP3 inflammasome in primary nasal epithelial cells (NECs) in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) and healthy controls.
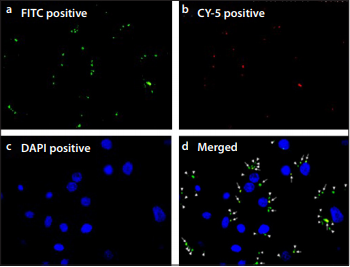
Material and Methods: Brush biopsies isolated from both patients and healthy controls were denoted respectively for our experiments. These were treated with S. aureus strains (four strains) only and in combination with budesonide (0, 10, 100, 1000 nM). NECs treated with only budesonide (0, 10, 100, 1000 nM) and untreated NECs were used as controls. Expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, IL-1β along with NLRC1/2 was analyzed by qPCR. Caspase-1 activity was measured by fluorogenic substrates Ac-YVAD-AMC. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA) assay was performed to measure IL-1β production.
Results: The mRNA levels of NLRC1, NLRC2, caspase-1, and IL-1β significantly increased, while NLRP3 demonstrated a trend toward elevation in the CRS group compared to the healthy controls. Infection with S. aureus increased caspase-1 activity and IL-1β secretion. However, treatment with budesonide decreased mRNA expression of NLRC2 and IL-1β secretion.
Conclusion: Increase in the caspase-1 activity and IL-1β levels, due to possible activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes, upon S. aureus infection, may have an important role in the pathogenesis of CRS.
Cite this article as: Saber A, Hussain R, Nakka S, Hugosson S. Effect of Staphylococcus Aureus on the NLRP3 Inflammasome, Caspase-1 and IL-1 β Expression in the Nasal Epithelial Cells in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Eur J Rhinol Allergy 2019; 2(1): 6-12.

.png)

.png)